Discovering the Body's Inner Network: A Journey Through the Endocannabinoid System
Welcome to this blog post where we will explore and delve into the body's fascinating endocannabinoid system (ECS). This biological network has been relatively unknown to the public, but its importance in regulating a range of functions in the body is incredibly important. From its discovery to its possible therapeutic uses, we will take an exciting journey through the world of ECS.
What is the Endocannabinoid System?
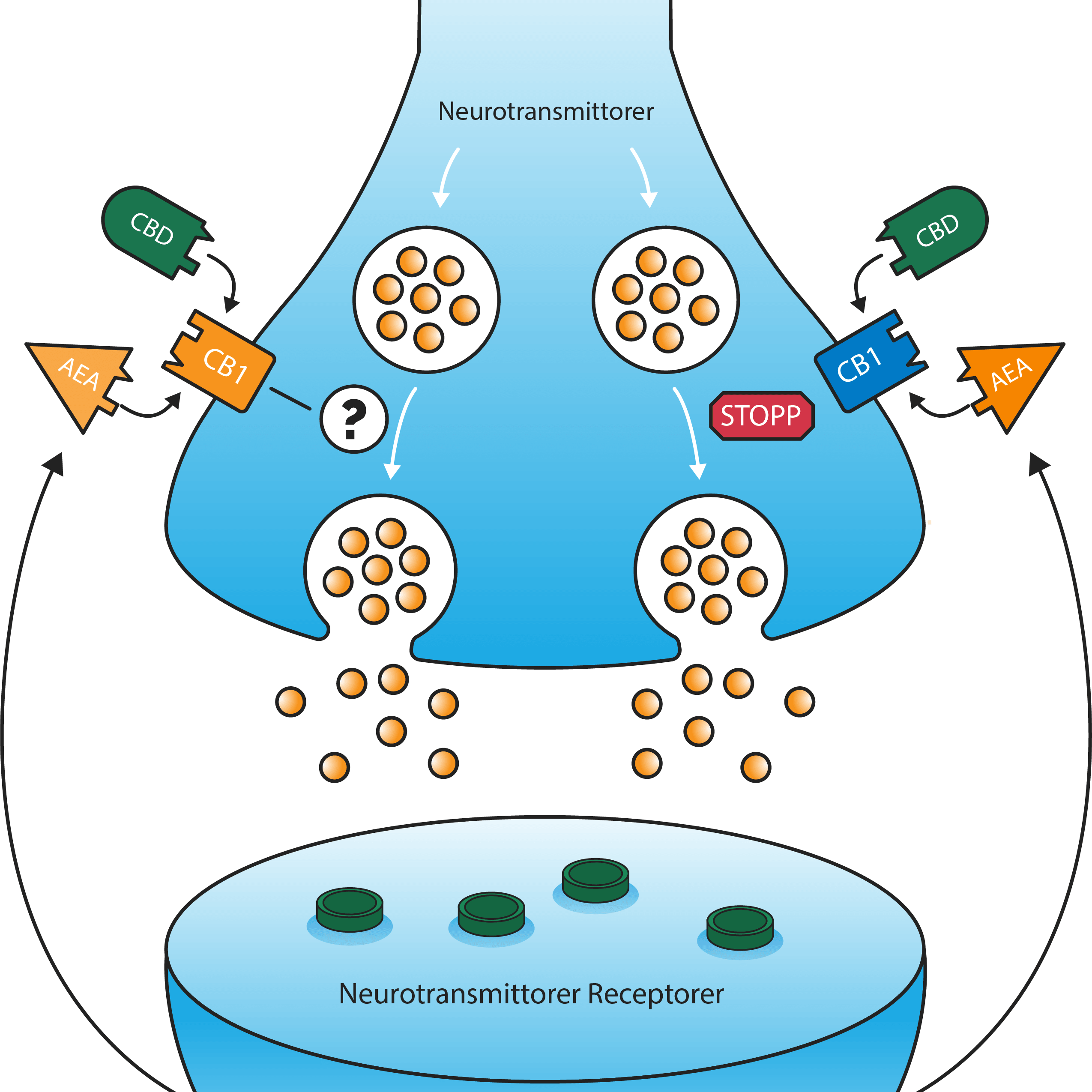
The endocannabinoid system is a complex cellular network found in all vertebrates, including humans. The ECS consists of endocannabinoids, receptors and degradation enzymes that work together to regulate various physiological processes in the body and ensure homeostasis (balance). The two main endocannabinoids that the body produces are anandamide and 2-arachidonoylglycerol (2-AG).
Receptors in ECS
There are two main types of cannabinoid receptors in the ECS: CB1 and CB2. CB1 receptors are found primarily in the brain and nervous system and are involved in functions such as pain relief, appetite regulation, cognitive function and memory. On the other hand, CB2 receptors are mainly found in the immune system and on peripheral tissues, where they play a role in regulating inflammation and immune function.
Endocannabinoids act as keys that fit into these receptors, triggering biochemical reactions that send signals throughout the body. These signals can have different effects depending on which type of endocannabinoid is involved and which type of receptor is activated.
Functions and Regulation of ECS
The endocannabinoid system is involved in a variety of functions in the body. One of its main tasks is to maintain homeostasis by balancing various systems, including the nervous system, the immune system, and the endocrine system. When any part of the body is out of balance, endocannabinoids are produced to restore balance.
ECS also regulates the stress response and plays an important role in managing reactions to stressful situations. In addition, the ECS has an effect on our mood and overall well-being.
The Discovery of ECS
The history of ECS is relatively recent, and its discovery is linked to research on cannabis. In 1964, Israeli researcher Raphael Mechoulam identified delta-9-tetrahydrocannabinol (THC) as the main psychoactive component of cannabis. This led researchers to begin investigating how THC interacted with the body.
In 1992, researchers Lisa Matsuda and her team discovered the first cannabinoid receptor CB1. In 1993, another research team led by William Devane and Allyn Howlett discovered an endocannabinoid called anandamide, which was shown to bind to the CB1 receptor. Later, the CB2 receptor and 2-AG, another important endocannabinoid, were discovered.
Therapeutic possibilities
Because the ECS affects so many biological functions, it has attracted interest in medical and scientific circles for its therapeutic potential. Research has shown that the ECS may play a role in the treatment of various diseases and conditions, including chronic pain, inflammatory diseases, epilepsy, anxiety and depression.
It has also been shown that cannabis and cannabinoids can affect the ECS by binding to its receptors and thereby have potential medicinal properties. Research in this area is still ongoing, and more extensive studies are needed to understand the exact mechanisms and potential for therapeutic use.
Summary
The body's endocannabinoid system is an incredibly complex and important biological network that regulates a range of physiological functions and helps maintain homeostasis. Its discovery has opened doors to research into its therapeutic potential, giving hope that future medical treatment may benefit from ECS functions. As research continues to develop, we can expect to learn even more about this fascinating system and its impact on our health and well-being.



Comments